
Yoga vs Meditation for Stress-Eating: What Actually Helps Curb Cravings?
What You’ll Learn
In this article, we’ll delve into:
– The effectiveness of Yoga and Meditation in reducing stress-induced eating.
– Which practice aligns best with your personal goals and lifestyle.
– Practical tips for integrating these practices into your daily routine.
Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | Yoga | Meditation for Stress-Eating |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to address stress-eating. | Mental techniques to enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation. |
| Accessibility | Requires physical space and equipment; classes may be in-person or online. | Can be practiced anywhere without special tools; available through various apps and online resources. |
| Community Support | Often involves group classes or guided sessions, fostering community support. | Can be practiced individually or in groups, offering flexibility in practice. |
Overview of Yoga
Yoga is an ancient practice that combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to promote overall well-being. It has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, which are often linked to emotional eating behaviors. ([health.harvard.edu](https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/yoga-for-weight-loss-benefits-beyond-burning-calories-202112062650?utm_source=openai))
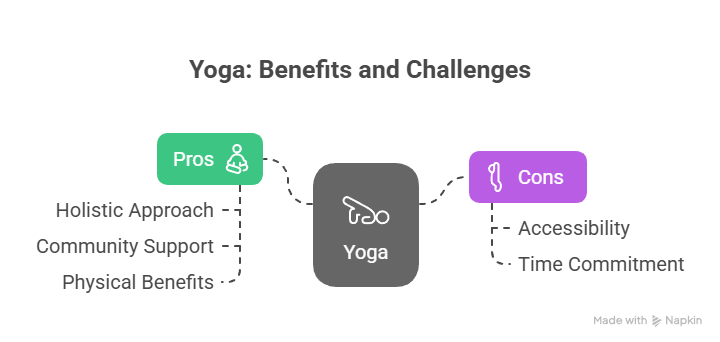
Pros
– **Holistic Approach**: Addresses both physical and mental aspects of stress-eating.
– **Community Support**: Group classes provide a sense of belonging and motivation.
– **Physical Benefits**: Improves flexibility, strength, and overall health.
Cons
– **Accessibility**: Requires physical space and equipment; classes may be in-person or online.
– **Time Commitment**: Regular practice may require a significant time investment.
Overview of Meditation for Stress-Eating
Meditation focuses on mental techniques to enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation, which can help in managing stress-induced eating habits. Practices like mindfulness meditation have been associated with reduced emotional eating. ([pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11776448/?utm_source=openai))
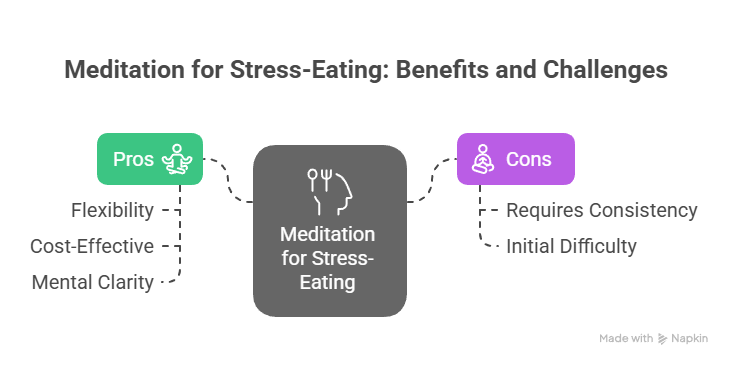
Pros
– **Flexibility**: Can be practiced anywhere without special tools.
– **Cost-Effective**: Many free or low-cost resources are available.
– **Mental Clarity**: Enhances self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Cons
– **Requires Consistency**: Regular practice is essential for effectiveness.
– **Initial Difficulty**: Beginners may find it challenging to focus during sessions.
Side-by-Side Breakdown
Effectiveness in Reducing Stress-Eating
Both yoga and meditation have been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, which are often linked to emotional eating behaviors. Yoga’s physical activity component may also help in reducing cravings. ([health.harvard.edu](https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/yoga-for-weight-loss-benefits-beyond-burning-calories-202112062650?utm_source=openai))
Target Audience
– **Yoga**: Suitable for individuals seeking a holistic approach to managing stress-eating through physical activity and mindfulness.
– **Meditation**: Ideal for individuals looking for mental techniques to address stress-eating by enhancing self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Pricing and Accessibility
– **Yoga**: Classes may range from $15 to $30 per session, with options for in-person or online participation. ([finmodelslab.com](https://finmodelslab.com/products/mindfulness-studio-marketing-mix?utm_source=openai))
– **Meditation**: Many free or low-cost apps and online resources are available, with some premium apps offering additional features.
Use Cases and Scenarios
– **Yoga**: Best for those who enjoy physical activity and prefer structured group settings.
– **Meditation**: Suitable for individuals seeking flexibility and the ability to practice independently.
Technical Specifications
– **Yoga**: May require physical space and equipment; classes may be in-person or online.
– **Meditation**: Can be practiced anywhere without special tools; available through various apps and online resources.
User Experience
– **Yoga**: Offers a community environment with group classes, fostering support and motivation.
– **Meditation**: Provides flexibility to practice individually or in groups, with various resources available online.
Which One Should You Choose?
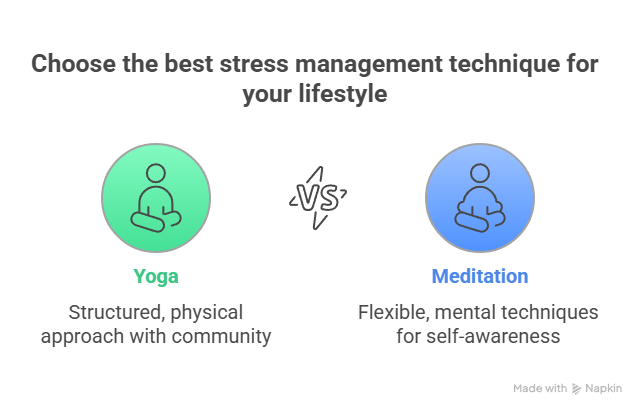
Your choice between yoga and meditation for managing stress-induced eating depends on your personal preferences and lifestyle:
– **Choose Yoga** if you prefer a structured, physical approach with community support.
– **Choose Meditation** if you seek flexibility and mental techniques to enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Yoga vs Meditation for Stress-Eating: The Final Verdict
| Category | Yoga | Meditation for Stress-Eating |
|——————————|———————————————————————-|——————————————————————|
| Best for Beginners | Yes, offers structured classes and community support. | Yes, with numerous beginner-friendly resources available. |
| Best for Power Users | Yes, advanced classes and practices available. | Yes, with deep practices for experienced meditators. |
| Best Value | Moderate cost per session; packages may offer savings. | Many free or low-cost options; premium apps available. |
Findings and Recap
Both yoga and meditation offer valuable tools for managing stress-induced eating. Your choice should align with your personal preferences, lifestyle, and goals.
Ready to take control of your eating habits? Explore our recommended resources to get started:
Related reading: Mindfulness Practices to Combat Emotional Eating
AI Image Prompt: A serene scene depicting a person practicing yoga in a tranquil studio, juxtaposed with another person meditating in a peaceful outdoor setting, both exuding calm and mindfulness.
“`html
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between Yoga and Meditation for Stress-Eating?
Yoga combines physical postures, breath control, and meditation to enhance mindfulness and reduce stress, which can help curb emotional eating. Meditation, on the other hand, focuses on mental practices to increase awareness and manage stress, also aiding in reducing stress-related eating behaviors. Both approaches offer unique benefits, and their effectiveness may vary depending on individual preferences and needs. ([bybsandthrive.com](https://www.bybsandthrive.com/post/yoga-vs-meditation-for-emotional-regulation-exploring-differences-and-similiarities?utm_source=openai))
Yoga enhances mindfulness, allowing individuals to become more aware of their body’s hunger and fullness cues, thereby reducing emotional and stress-induced eating. Specific yoga poses and breathing techniques can also lower cortisol levels, mitigating stress that often triggers overeating. ([health.harvard.edu](https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/yoga-for-weight-loss-benefits-beyond-burning-calories-202112062650?utm_source=openai))
Can Meditation effectively reduce stress-induced eating habits?
Yes, meditation, particularly mindfulness meditation, has been shown to increase awareness of eating habits and emotional triggers, leading to a reduction in stress-related eating behaviors. By fostering a non-judgmental awareness of thoughts and emotions, meditation helps individuals make conscious food choices and manage cravings. ([pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10973375/?utm_source=openai))
Which practice is more suitable for someone new to stress management techniques?
For beginners, meditation may be more accessible as it requires minimal physical activity and can be practiced anywhere. It focuses on mental clarity and stress reduction, which can be beneficial for managing stress-induced eating. Yoga, while also effective, involves physical postures and may require more time and space to practice. ([bybsandthrive.com](https://www.bybsandthrive.com/post/yoga-vs-meditation-for-emotional-regulation-exploring-differences-and-similiarities?utm_source=openai))
Integrating both yoga and meditation can provide a holistic approach to managing stress-related eating. Yoga offers physical benefits and enhances body awareness, while meditation improves mental focus and emotional regulation. Together, they can address both the physical and psychological aspects of stress-induced eating behaviors. ([yogawestcollective.com](https://yogawestcollective.com/yoga-and-eating-finding-harmony-for-body-and-mind/?utm_source=openai))
Are there specific Yoga poses that help reduce stress-induced eating?
Yes, certain yoga poses, such as Child’s Pose (Balasana), Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose (Viparita Karani), and Corpse Pose (Savasana), are known to lower cortisol levels and promote relaxation, which can help reduce stress-induced eating. Incorporating these poses into your routine may aid in managing stress-related eating behaviors. ([patanjaleeyoga.com](https://patanjaleeyoga.com/how-does-yoga-help-curb-emotional-eating/?utm_source=openai))
The time frame to observe results can vary depending on individual commitment and consistency. Some individuals may notice improvements in stress levels and eating habits within a few weeks of regular practice, while others may require several months. It’s important to approach these practices with patience and consistency to achieve the best outcomes. ([psychologytoday.com](https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the-science-of-willpower/201007/how-yoga-can-help-end-binge-eating?utm_source=openai))
“`